Mortality caused by heatwaves in China has increased since 1979
Since the beginning of the summer in 2022, China has been sweltering under the worst heatwave in decades. A number of people in Zhejiang, Henan, Jiangsu, and Sichuan provinces were diagnosed with thermoplegia, the most severe form of heatstroke, and some have died of this disease.
In a warming world, the threat of heatwaves to human health is increasing. Researchers led by Dr. Zhao Liang from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. Huang Cunrui from Tsinghua University investigated the spatial and temporal variation of heatwave-related human deaths in China from 1979 to 2020.
The study was published in Science Bulletin.
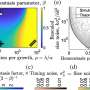
They also explored the relative contributions of drivers such as heatwave exposure, population growth, population aging, and baseline mortality to changes in attributable mortality.
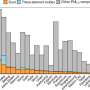
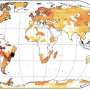
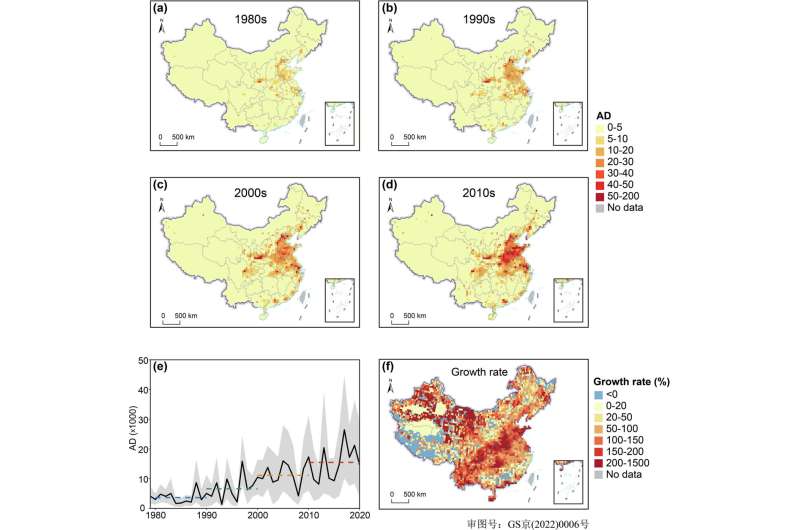
"We found that the number of deaths caused by heatwaves in China has increased rapidly since 1979, from 3,679 persons per year in the 1980s to 15,500 persons per year in the 2010s," said Dr. Zhao. "We also found strong spatial heterogeneity across the country, with more human deaths in East and Central China."
Then what are the main drivers of the large increase in heatwave-related deaths in China over the past four decades?
"The main drivers are the rapid increase in the frequency of heatwaves, followed by population growth, population aging, and rising baseline mortality. From the 2000s to the 2010s, these four factors accounted for 40.6%, 22.4%, 20.8%, and 16.2% of the change in attributed human deaths, respectively," said Prof. Huang.
The research team hopes this study's accurate assessment of the number of heatwave-related deaths in China and the contribution of their different drivers can help policy makers to fully understand human health hazards of heatwaves and to develop response policies to reduce health losses from increased heatwave exposure under climate change.
More information: Huiqi Chen et al, Spatiotemporal variation of mortality burden attributable to heatwaves in China, 1979–2020, Science Bulletin (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2022.05.006
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences