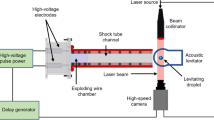
Abstract
Gravity is commonly considered negligible when the surface tension is dominant; i.e., the Bond number is less than 1. In this paper, however, the authors present a technique in which drops slide over surfaces with zero effective gravity. Our study compared the sliding motion of water drops on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces in scenarios: one in which effective gravity = 1 (1 g) and one in which it = 0 (0 g). The authors found that the lateral retention force was greater under 1 g than it was under 0 g. Also, the results showed that retention forces calculated by Furmidge equation are higher than the measured forces.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Schaerli, R.C. Wootton, T. Robinson, V. Stein, C. Dunsby, M.A.A. Neil, P.M.W. French, A.J. DeMello, C. Abell, and F. Hollfelder: Continuous-flow polymerase chain reaction of single-copy DNA in microfluidic microdroplets. Anal. Chem. 81, 302–306 (2009).
B. Teste, A. Ali-Cherif, J.L. Viovy, and L. Malaquin: A low cost and high throughput magnetic bead-based immuno-agglutination assay in confined droplets. Lab. Chip 13, 2344–2349 (2013).
X. Casadevall i Solvas and A. DeMello: Droplet microfluidics: recent developments and future applications. Chem. Commun. 47, 1936–1942 (2011).
D. Bogojevic, M.D. Chamberlain, I. Barbulovic-Nad, and A.R. Wheeler: A digital microfluidic method for multiplexed cell-based apoptosis assays. Lab. Chip 12, 627–634 (2012).
S. Cho, D.-K. Kang, S. Sim, F. Geier, J.-Y. Kim, X. Niu, J.B. Edel, S.-I. Chang, R.C.R. Wootton, K.S. Elvira, and A.J. DeMello: Droplet-based microfluidic platform for high-throughput, multi-parameter screening of photosensitizer activity. Anal. Chem. 85, 8866–8872 (2013).
D. Brutin, B. Sobac, B. Loquet, and J. Sampol: Pattern formation in drying drops of blood. J. Fluid Mech. 667, 85–95 (2011).
J.A. Lim, W.H. Lee, H.S. Lee, J.H. Lee, Y.D. Park, and K. Cho: Self-organization of ink-jet-printed triisopropylsilylethynyl pentacene via evaporation-induced flows in a drying droplet. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18, 229–234 (2008).
R.F. Allen, and P.R. Benson: Rolling drops on an inclined plane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 50, 250–253 (1975).
M. Sakai, J.-H. Song, N. Yoshida, S. Suzuki, Y. Kameshima, and A. Nakajima: Direct observation of internal fluidity in a water droplet during sliding on hydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 22, 4906–4909 (2006).
M. Sakai, A. Hashimoto, N. Yoshida, S. Suzuki, Y. Kameshima, and A. Nakajima: Image analysis system for evaluating sliding behavior of a liquid droplet on a hydrophobic surface. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 045103 (2007).
S. Suzuki, A. Nakajima, M. Sakai, Y. Sakurada, N. Yoshida, A. Hashimoto, Y. Kameshima, and K. Okada: Slipping and rolling ratio of sliding acceleration for a water droplet sliding on fluoroalkylsilane coatings of different roughness. Chem. Lett. 37, 58–59 (2008).
M. Sakai, J.-H. Song, N. Yoshida, S. Suzuki, Y. Kameshima, and A. Nakajima: Relationship between sliding acceleration of water droplets and dynamic contact angles on hydrophobic surfaces. Surf. Sci. 600, L204–L208 (2006).
H. Ren, S. Xu, and S.T. Wu: Effects of gravity on the shape of liquid droplets. Opt. Commun. 283, 3255–3258 (2010).
S. Vafaei and M.Z. Podowski: Analysis of the relationship between liquid droplet size and contact angle. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 113, 133–146 (2005).
L.-J. Yang, T.-J. Yao, and Y.-C. Tai: The marching velocity of the capillary meniscus in a microchannel. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 220–225 (2004).
W.H. Hager: Wilfrid Noel Bond and the Bond number. J. Hydraul. Res. 50, 3–9 (2012).
V.A. Lubarda and K.A. Talke: Analysis of the equilibrium droplet shape based on an ellipsoidal droplet model. Langmuir 27, 10705–10713 (2011).
D.H. Shin, S.H. Lee, J.-Y. Jung, and J.Y. Yoo: Evaporating characteristics of sessile droplet on hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces. Microelectron. Eng. 86, 1350–1353 (2009).
S. Ravi Annapragada, J.Y. Murthy, and S. V. Garimella: Droplet retention on an incline. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55 (5–6), 1457–1465 (2012).
S. Tang, Y. Bhimavarapu, S. Gulec, R. Das, J. Liu, H. N'Guessan, T. Whitehead, C.W. Yao, and R. Tadmor: Droplets sliding down a vertical surface under increasing horizontal forces. Langmuir 35, 8191–8198 (2019).
C.-W. Yao, S. Tang, D. Sebastian, and R. Tadmor: Sliding of water droplets on micropillar-structured superhydrophobic surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 144493 (2019). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144493.
D. Quéré, M.-J. Azzopardi, and L. Delattre: Drops at rest on a tilted plane. Langmuir 14, 2213–2216 (1998).
G. Pu, J. Ai, and S.J. Severtson: Drop behavior on a thermally-stripped acrylic polymer: influence of surface tension induced wetting ridge formation on retention and running. Langmuir 26, 12696–12702 (2010).
S. Daniel, M.K. Chaudhury, and J.C. Chen: Fast drop movements resulting from the phase change on a gradient surface. Science 291, 633–636 (2001).
Y. Zheng, H. Bai, Z. Huang, X. Tian, F.Q. Nie, Y. Zhao, J. Zhai, and L. Jiang: Directional water collection on wetted spider silk. Nature 463, 640–643 (2010).
W. Wang, J.V.I. Timonen, A. Carlson, D.M. Drotlef, C.T. Zhang, S. Kolle, A. Grinthal, T.S. Wong, B. Hatton, S.H. Kang, S. Kennedy, J. Chi, R.T. Blough, M. Sitti, L. Mahadevan, and J. Aizenberg: Multifunctional ferrofluid-infused surfaces with reconfigurable multiscale topography. Nature 559, 77–82 (2018).
R. Tadmor, A. Baksi, S. Gulec, S. Jadhav, H.E. N'guessan, V. Somasi, M. Tadmor, S. Tang, P. Wasnik, and S. Yadav: Defying gravity: Drops that climb up a vertical wall of their own accord. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 562, 608–613 (2020).
S. Basu, K. Nandakumar, and J.H. Masliyah: A model for detachment of a partially wetting drop from a solid surface by shear flow. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 190, 253–257 (1997).
H. Sakai and T. Fujii: The dependence of the apparent contact angles on gravity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 210, 152–156 (1999).
R. Tadmor, P. Bahadur, A. Leh, H.E. N'Guessan, R. Jaini, and L. Dang: Measurement of lateral adhesion forces at the interface between a liquid drop and a substrate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 266101 (2009).
P.S. Wasnik, H.E. N'guessan, and R. Tadmor: Controlling arbitrary humidity without convection. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 455, 212–219 (2015).
C.G.L. Furmidge: Studies at phase interfaces. I. The sliding of liquid drops on solid surfaces and a theory for spray retention. J. Colloid Sci. 17, 309–324 (1962).
S. Varagnolo, D. Ferraro, P. Fantinel, M. Pierno, G. Mistura, G. Amati, L. Biferale, and M. Sbragaglia: Stick-slip sliding of water drops on chemically heterogeneous surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 066101 (2013).
N. Gao, F. Geyer, D.W. Pilat, S. Wooh, D. Vollmer, H.J. Butt, and R. Berger: How drops start sliding over solid surfaces. Nat. Phys. 14, 191–196 (2018).
E.B. Dussan V and R.T.P. Chow: On the ability of drops or bubbles to stick to non horizontal surfaces of solids. J. Fluid Mech. 137, 1–29 (1983).
C.W. Extrand and A.N. Gent: Retention of liquid drops by solid surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 138, 431–442 (1990).
R.A. Brown, F.M. Orr, and L.E. Scriven: Static drop on an inclined plate: Analysis by the finite element method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 73, 76–87 (1980).
A.I. ElSherbini and A.M. Jacobi: Retention forces and contact angles for critical liquid drops on non-horizontal surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 299, 841–849 (2006).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Center for Midstream Management and Science (CMMS) of Lamar University. The authors also appreciate the Center for Innovation, Commercialization and Entrepreneurship (CICE) at Lamar University for providing lab space.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary material
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2020.40.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, S., Yao, CW., Tadmor, R. et al. Lateral retention of water droplets on solid surfaces without gravitational effect. MRS Communications 10, 449–454 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2020.40
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2020.40